The finish and appearance of a hot dip galvanized coating is dynamic, a ‘living’ surface that visibly changes until the hot dip galvanized surface attains a stable zinc patina or zinc carbonate film which is a dense insoluble film dull-grey in colour.
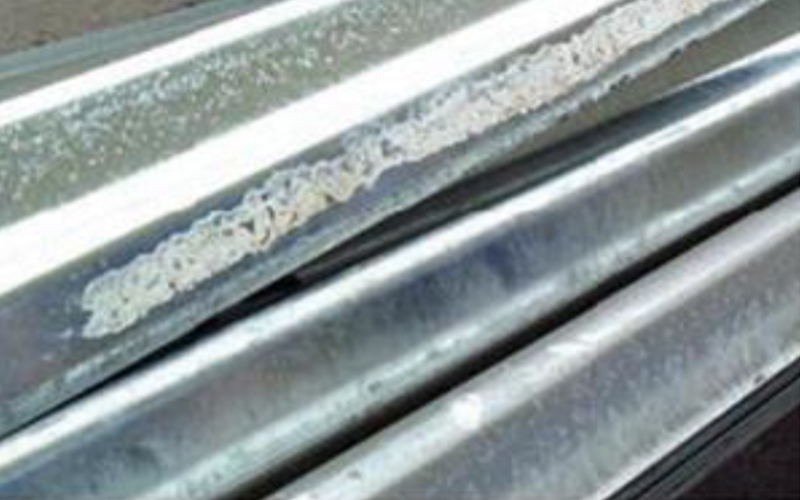
Wet storage staining or white rust occurs when galvanized materials are closely nested or tightly stacked with moisture entrapped between them and there is inadequate airflow across the zinc surfaces. Examples of this may be found when galvanized materials have been exposed to rain, condensation or high-humidity atmospheric conditions and have remained wet for an extended period of time. Once the hot dip galvanized components are separated and dried out, the formation of white rust ceases.
White-rust is a post-galvanizing phenomenon. Prevention thereof lies in the manner materials are packed and stored prior to installation and use. The presence of white rust is not a reflection on the galvanized coating’s performance. By ensuring that the causes of white-rust are recognised and the risks of its occurrence minimized it is avoidable and easily managed by all parties involved in the supply chain.