Used by the HDGASA to determine Service Life of Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Exposed
to Various Atmospheric Environments
Reference Source: ISO 9223:2012
Summary of ISO 9223 Specification
The ISO 9223 specification considers key factors in determining the atmospheric corrosion
rate of carbon steel, zinc, copper and aluminium. These factors are:
1) Time of wetness, Table B.1 – Classification of time of wetness (t) being the period
that the zinc surface is covered by liquid containing the corrosive elements
(Electrolyte).
2) Outdoor concentration, Table B.2 – Some of the most important range of pollutants
3) Pollution by sulphur containing substances represented by (SO2, Table B.3
4) Airborne pollution containing salinity, Table B.4 – represented by chloride usually in
the form of chlorides carried in the prevailing winds from off the sea.
NB: This information sheet will only consider the corrosion rates of zinc.
Classification of atmospheric corrosivity include three additional ISO specifications, these
are:
1. Guiding corrosion values of each category for specific metals ISO 9224
2. Measurement of environmental parameters affecting atmospheric corrosivity ISO 9225
and
3. Determination of corrosion loss on standard specimens ISO 9226
Tables used in the Development of the Atmospheric Classifications
(Reference source ISO 9223:2012)
Various tables are published within the ISO 9223:2012 specifications and are listed here
for reference purposes. Detailed data pertaining to each of these tables are contained
within the ISO 9223:2012 specification.
Table B.1 – Time of wetness in different exposure conditions (t)
Table B.2 – Outdoor concentration of some of the most important pollutants in different
types of environments (a range of pollutants)
Table B.3 – Grouping of pollution by sulphur containing substances represented by SO2
Table B.4 – Grouping of pollution by airborne salinity represented by chloride
Table C.1 – Description of typical atmospheric environments related to the estimation of
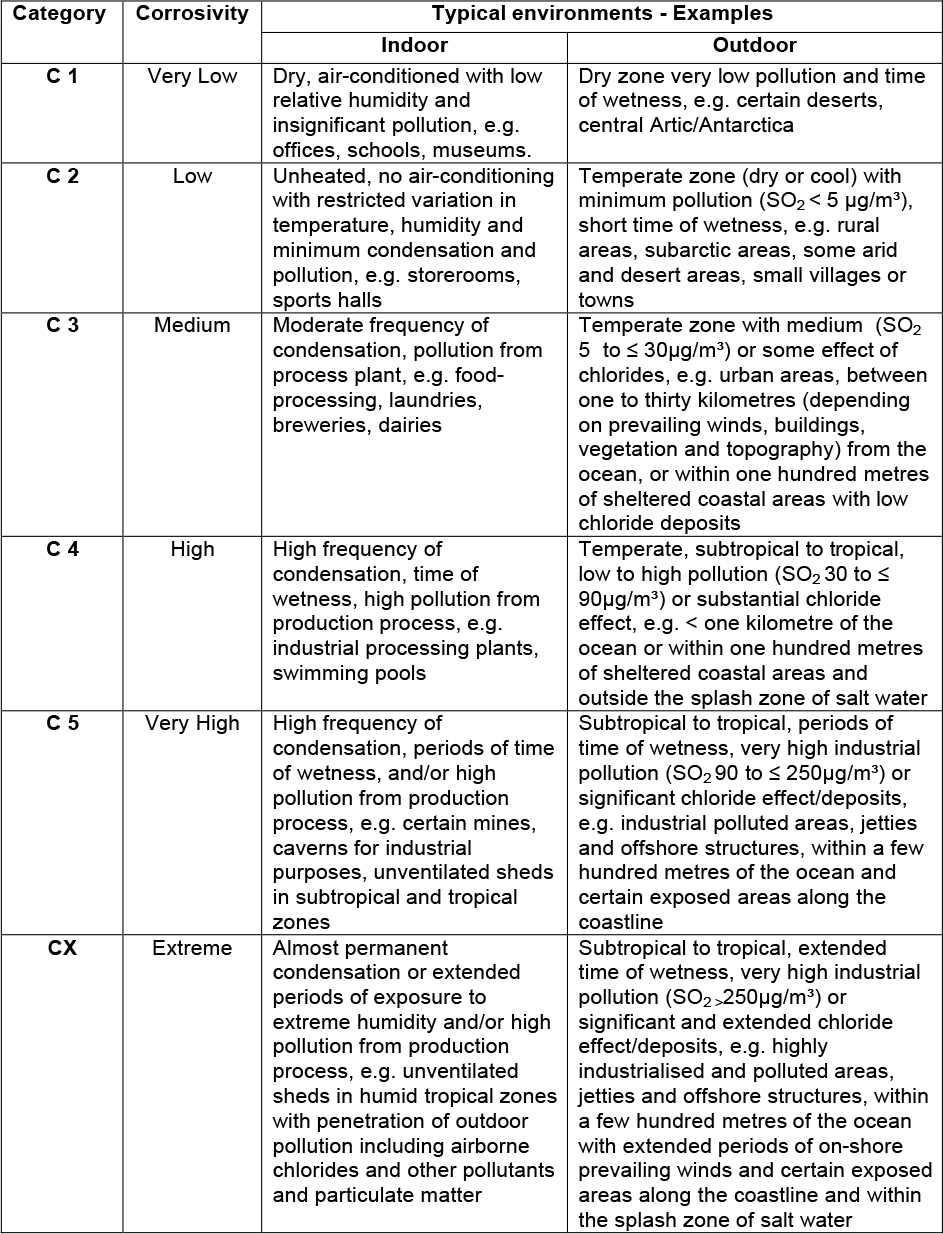
The typical descriptions detailed in Table 1 are intended as a general guide only and it is recommended that a review of actual site conditions should be undertaken before finalising the applicable corrosive category. A general review of existing hot dip galvanized structures is an ideal method used to establish the corrosive conditions in the general area of a particular site.
Table 2 – Estimated Service Life for Hot Dip Galvanized Steel (Zinc) complying with SANS 121 (ISO 1461:2009) and subjected to Atmospheric Environments Classified in terms of ISO 9223:2012
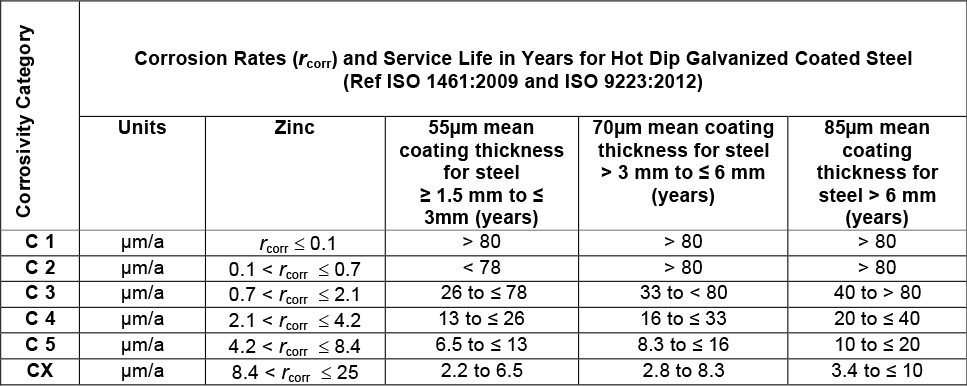
The conservative and wide range of service life estimates shown in Table 2 are only
intended as a general guide. It is a recommended requirement that a more detailed
assessment of the actual site environmental conditions should be investigated in order to
refine longevity expectations for hot dip galvanized carbon steel.
Duplex Systems
Duplex systems (hot dip galvanizing plus a suitable paint system) provide synergy by virtue
of the fact that the durability of the combined hot dip galvanized substrate and top organic
coating system is greater than the sum of the separate durability’s of the two forms of
corrosion control.
Synergistic effect can be estimated mathematically as follows:
Duplex Life = factor x (zinc life + paint life)
Table 3 – Synergistic Protection Provided by the Combined use of a Zinc Coating
and a Paint Coating. (Refer Jan van Eijnsbergen and Porter)
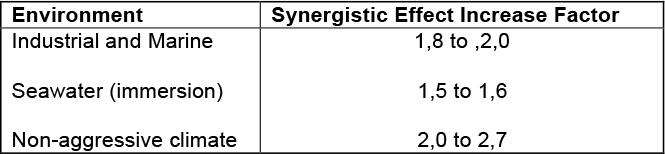
The synergy factors vary from 1,5 in the extreme corrosive environments to 2,7 in less- aggressive environments. In a highly aggressive environment (ISO 9223:2012 C4, C5 and CX corrosivity categories) hot dip galvanizing on its own tends to become marginal in terms of service life. Duplex systems have been shown to provide a significant service life extension. On the bases of the synergistic effect increase factor of 1.5, table 4 has been
developed.
Table 4 – Estimated Service Life for Duplex system (zinc plus paint) Complying with SANS 121 (ISO 1461:2009) and Subjected to Atmospheric Environmental Classified in terms of ISO 9223:2012
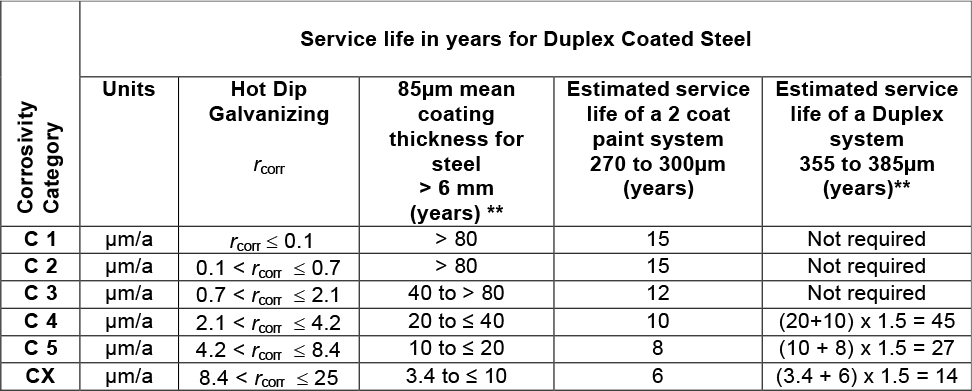
** Assumes the worst case in terms of hot dip galvanizing figures used in calculating Duplex service life. The document “Duplex Coating – An overview”, is available from the Association